Understanding and analyzing 2D/3D images
From basic information to analysis of digital image which produced from industrial/medical X-ray CT, microscopes, SEM, TEM and other digital imaging devices.
Basic Information
2D/3D
2D (slice) data is like photo.
A collection of successive photos is called 3D (volume) data.
The minimum unit is called pixel in 2D and voxel in 3D.
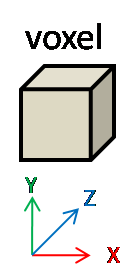
pixel is 2D data (planar) and exists X and Y axes.
voxel is 3D data (solid) and exists X, Y and Z axes.
Axes displayed by color, generally
RGB
(Red, Green, Blue)
X (Red),
Y (Green),
Z (Blue)
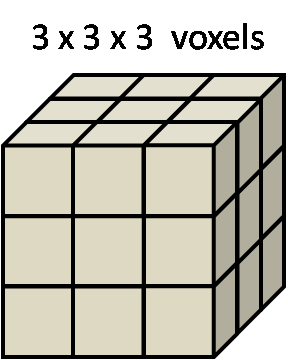
Describe above voxel data
data size: 3 x 3 x 3
voxel size: 2 x 2 x 2 cm
voxel unit: 1 byte (8 bits)
(voxel size used as resolution or spacing
If understand the concepts, you will catch up the meaning by any expressions.)
voxel size calls single voxel. (the smallest measure = resolution = minimum separable space)
Data size on media such as in memory is 3 x 3 x 3 x 1(byte) = 27 bytes
If voxel unit is 2 bytes, the data size will be 3 x 3 x 3 x 2(byte) = 54 bytes
single voxel size is 2 x 2 x 2 cm = 8 cm3
so real size of data is 8 x 27 = 216 cm3
Basic and widely used terms
Intensity histogram
ROI (Region of Interest)
Segmentation
Labeling